
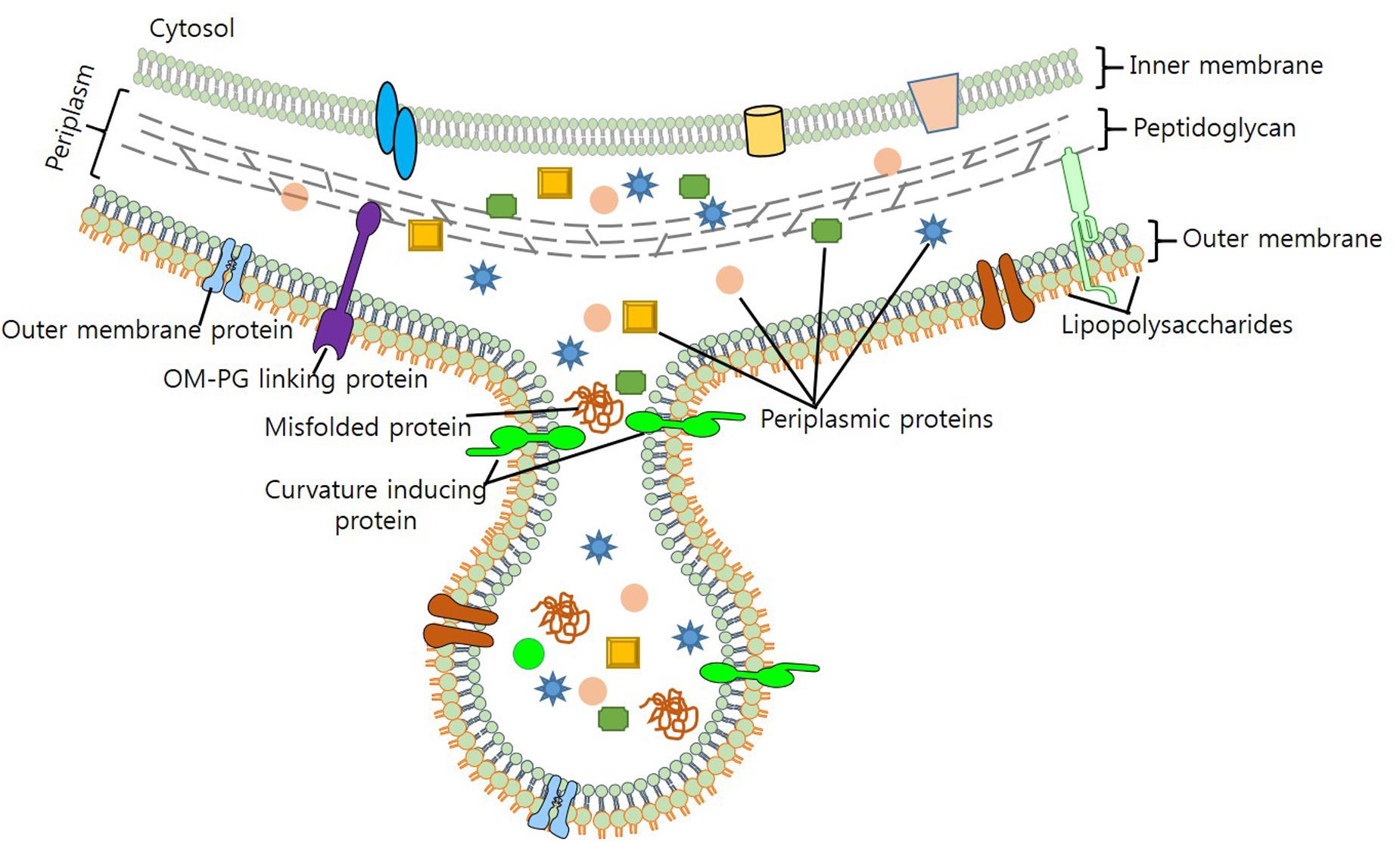
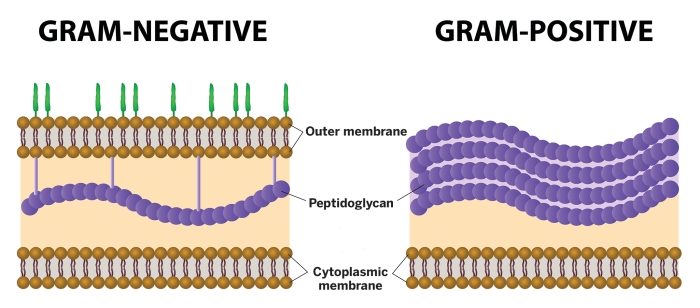
The so-called peripheral membrane proteins remain firmly associated with the membrane surfaces. Other proteins have one portion that is anchored in the membrane and extra-membrane regions that point into or out of the cell. Many membrane proteins are firmly embedded in the membrane and are named integral membrane proteins. The cytoplasmic membranes of some bacteria are strengthened by molecules called hopanoids, which are rigid planar molecules and structural analogs of sterols. The structure is fluid and the proteins that are immersed in the phospholipid bilayer can undergo both rotational and lateral movement. The membrane has a thickness of 6–8 nm and can be seen using an electron microscope: it appears as two dark-colored lines (glycerophosphate) that are separated by a lighter area (fatty acids). In the phospholipid membrane, the fatty acids point inward toward each other to form the hydrophobic environment, while the hydrophilic portion remains exposed to the external environment or the cytoplasm. The membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer: phospholipids contain both hydrophobic (fatty acid) and hydrophilic (glycerol-phosphate) components. The cytoplasmic membrane is a thin barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular environment. Gram-positive bacteria do not have an outer membrane and their wall is mainly composed of a thick layer of peptidoglycan. The outer membrane acts as a barrier against the diffusion of many compounds, making the cell more resistant to toxic substances. In the inter-membrane space, there is a thin layer of peptidoglycan (or murein), referred to as the periplasm, a complex polymer that is made up of amino sugars and amino acids that completely envelop the cell. In the gram-negative cell wall, a lipid bilayer membrane, the outer membrane (OM) is present, while the above-mentioned plasma membrane is the inner membrane (IM). The plasma membrane is covered by a wall with different characteristics, leading to the well-known division into gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The cell is surrounded by the plasma membrane, which regulates the transport of nutrients and waste substances. Among them, pathogens represent a small percentage of the entire known bacterial population.īacteria are unicellular organisms that are formed by a prokaryotic cell, with dimensions ranging from 0.2 to 2 µm. Based on the bacterium-host relationship, these microorganisms can be divided into four categories: symbionts, that live and multiply in contact with the host without causing damage and establishing a beneficial reciprocal relationship diners that live and multiply in contact with the host without causing damage pathogens that take advantage of the host causing diseases, from mild to serious ones and opportunists, which normally are harmless but can cause disease, even serious ones if a weakening of the defense system of the organism occurs. Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and autism have been studied for a putative role of microbiota in their development. Currently, the connections between the human body and the microbiome are not limited to the gastrointestinal or immune system but concern almost all other systems. This has led to investigations of the mechanisms that link autoimmune diseases or allergies to changes in the microbiome. The intestinal microbiota plays a central role in the development of the immune system and the modulation of its function. They populate the resident flora, or “microbiota”, are essential to facilitate food digestion or prevent the proliferation of other more dangerous bacteria, and acting as saprophytes. Bacteria also live in the human and animal bodies, particularly on the skin, airways, oral cavity, and the digestive, reproductive, and urinary systems, normally without causing any harm. In industrial microbiology, microorganisms are grown on a large scale to produce compounds such as antibiotics, enzymes, and various chemicals, while in biotechnology, genetically-modified organisms are used to synthesize, for example, human proteins for medical use. In the food industry area, bacteria are involved in the manufacturing of many products, including dairy products, baked goods, and alcoholic beverages. The bacterial fermentation process is also fundamental for the digestive systems of sheep and cattle.
Moreover, nitrogen-fixing bacteria are essential for the natural growth of several plant species.
The worldwide bacterial population is estimated to reach 2 × 10 30 cells, with a major role in the ecosystem. They can be found in the soil, ocean water, ice, and underneath the earth’s crust that is because these microorganisms are often essential to other organisms’ life. Bacteria are microscopic single-celled organisms that are listed among the oldest known life forms on Earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
